How to make AdWords campaign structure
When it comes to working with Google, we always focus on maximizing budget, giving that little boost to CTR or increasing impressions. Focusing on KPIs to improve the performance of our digital marketing campaigns is crucial. You should prepare a perfect AdWords campaign structure. What if we had to stop and take a couple of steps back?
AdWords campaign structure campaigns based on user
Paying attention to the needs and the user’s phase in the Customer Journey, we see 3 main phases in which we can influence our campaigns. Of course, the keywords and the bids that are made for them will change. In general, the more transactional the keyword, the more expensive the bid.
How do I set up my campaigns with the user in mind?
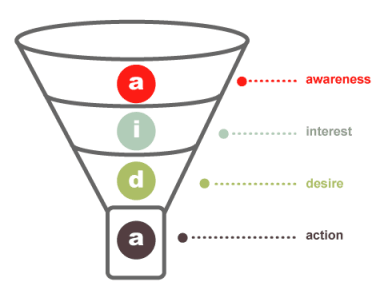
Starting from the AIDA model, it could be summarized in something like this:
Keywords> Relevant copy> relevant landing page
Informational search
Transactional search
Experiential search
And … what do we do with remarketing?
This is where the strong point comes in:
In any of the searches, the user can be marked the moment they enter the web page to increase the bid of our ads for users who have already gone through it.
For example, suppose someone has done a couple of informational searches to investigate which flowers might be the most interesting. In that case, we can set up a retargeting audience so that the moment that person switches to a transactional search, our ad is more likely to appear.
The effectiveness of this strategy is based on a logical argument:
Who is most likely to convert?
- User A
The classic campaign model. After several searches, a user has looked at blogs and has decided to look at a place to buy searches for “flower shop” and clicks on the first 3 results to find a place to buy.
- User B
Applying the user experience. A user who performs informational searches and visits the ABC website because an ad has appeared informing about the types of flowers. After several similar searches, he decides to buy and switches to a transactional search “ABC near me,” in which Floristería Manoli appears and several other sites that do not ring a bell.
You will most likely convert with the second option, since at the time of closing the transaction, it is more likely that you will decide on a company that you have already visited and that you know, to a completely unknown store.
User is the key
By focusing entirely on improving KPIs, we forget to think about the user, behave with our ads and, sometimes, more importantly, with our landing pages. Is a user looking for types of flowers the same as one looking for florist sites?
The first would be conducting an informational search. It is investigating the types of the product and its characteristics, a type of search in which the user focuses on reflection and curiosity, is considering the options.
On the other hand, the second user performs a transactional search, he is not considering the types of products but is investigating were to close the purchase in the most effective way: by proximity, price, quality.
In both cases, both the ad in Google Ads and the landing that both users reach should not be the same. Not even the keywords they use will be the same (although similar).
Share the experience
After the closing of the sale, it is essential to give tools to the consumer so that they can share their experience, we have several options, all of them widely used:
- Mail marketing: Send an email suggesting that you leave your opinion on the platforms.
- Google Business: Have it well configured, with description, texts and images to give a vivid image of the company.
- Social Networks: Facebook has the option to rate the business by stars. If you manage your social network well, you can invite people to rate you.
In the end, this process of sharing the experience will generate a value argument (Social Proof) to new and returning customers to make more purchases.
Campaigns in AdWords
At the campaign level, you will establish the daily budget, the geographical locations where you want your ads to be seen, the time schedules and other settings that will directly affect your results.
You must keep the following tips in mind when creating campaigns:
- Each campaign that you create must have a single business objective. You can’t search for conversions at the same time as branding, for example.
- Use a meaningful and descriptive vocabulary. “Campaign 1” is not a name for a campaign. The names must let you know what the campaign is about, for example: «Search_Shoes for Women.»
- Each campaign must be focused on a type of product. It is also important or recommended that each campaign contains homogeneous products in terms of their price. That is, you should not put in the same campaign products whose sale price is very different.
Ad groups and keywords
Ad groups are a set of two or more ads that group keywords that must be related to each other. Segment everything you can so that your ads are very relevant to your users’ searches and thus, you can increase your CTR and your quality level.
Imagine that you advertise running shoes: the typical mistake is to create a single campaign with an ad group and include words such as sneakers, running shoes, athletic shoes, sports … a priori it may seem correct, but if we want to have maximum relevance, it is best to create an ad group that is well-targeted.











Post Comment